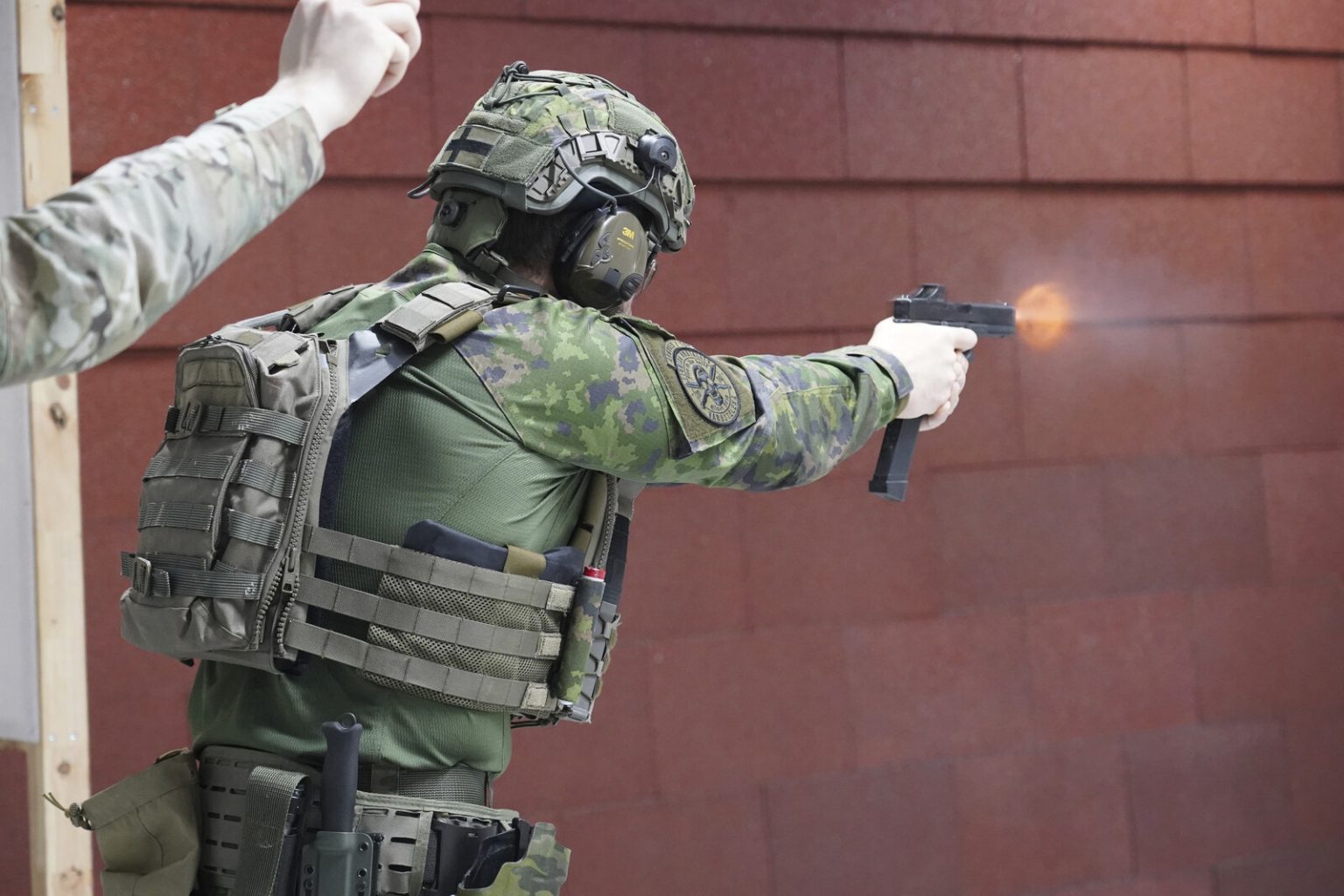
Finland, sharing a substantial 1,340-kilometer land border with Russia, has experienced a profound shift in its security perspective following Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine. This heightened awareness of potential threats has manifested in both significant geopolitical decisions and individual actions, solidifying Finland’s commitment to national defense. The nation’s accession to NATO, alongside Sweden, represents a fundamental realignment in its foreign policy, signifying a decisive move towards collective security and a departure from its previous stance of military non-alignment. Simultaneously, a surge in interest among Finnish citizens in acquiring firearms proficiency underscores a growing desire for personal preparedness in the face of potential conflict. This sentiment is encapsulated by Antti Kettunen’s analogy to learning to swim – a skill best acquired proactively, rather than in the face of immediate necessity. This resonates with the Finnish population’s pragmatic approach to defense, mirroring their long-standing tradition of national service and preparedness.
The escalating interest in firearms training is reflected in the rapid growth of organizations like the Vantaan Reservilaiset (Vanda Reservists), which has witnessed a doubling of its membership in just two years. Their repurposing of a former industrial facility highlights the tangible efforts being made to accommodate the increased demand for training spaces. This groundswell of interest is further supported by the Finnish government’s ambitious plan to establish over 300 new shooting ranges nationwide, significantly augmenting the existing 670 facilities. This initiative underscores the state’s commitment to facilitating citizen preparedness and reflects the broad societal consensus on the importance of national defense. Jukka Kopra, chairman of the Finnish parliament’s defense committee, aptly summarizes the national sentiment, emphasizing the historically strong defense consciousness in Finland, which has been further intensified by the current geopolitical climate. The war in Ukraine serves as a stark reminder of the potential for regional instability, driving home the importance of a prepared and vigilant citizenry.
Unlike Sweden, which maintains a Home Guard, Finland relies on a civil defense system managed by the Defense Training Association (MPK). The significant rise in participation in MPK training programs, more than doubling over the past three years, mirrors the surge in interest in firearms training. This increase in participation is indicative of a broader societal commitment to preparedness, with citizens actively seeking training to contribute to national defense. While motivations may vary, the underlying current of concern about regional stability undoubtedly plays a significant role. Miikka Kallio, a firefighter participating in shooting training, acknowledges the spectrum of motivations, ranging from recreational enjoyment to a more serious focus on preparedness.
The influx of new members into reservist organizations and the increased engagement with civil defense training suggests that concerns about Russia’s actions in Ukraine are a key driver for many Finns seeking to enhance their defense capabilities. While some engage in training for recreational purposes, the overarching context of regional instability and the desire to contribute to national security is palpable. This proactive approach to preparedness reflects a deeply ingrained sense of responsibility for national defense, a characteristic deeply embedded in Finnish culture and history. The collective response to the evolving geopolitical landscape demonstrates a nation united in its commitment to safeguarding its sovereignty and security.
The Finnish experience underscores the profound impact of geopolitical events on national consciousness and individual behavior. The war in Ukraine has served as a catalyst, prompting Finland to reassess its security posture and prompting citizens to take proactive steps to enhance their preparedness. The confluence of geopolitical strategy, reflected in NATO membership, and grassroots initiatives, exemplified by the surge in firearms training and civil defense participation, reveals a nation united in its commitment to national security. Finland’s response exemplifies a comprehensive approach to defense, integrating national policy with individual action, creating a robust and resilient national security framework.
In essence, Finland’s response to the altered geopolitical landscape demonstrates a multifaceted approach, combining strategic alliances with individual preparedness. The nation’s accession to NATO signifies a decisive shift in its foreign policy, while the increasing interest in firearms training and civil defense participation reflects a growing sense of individual responsibility for national security. This comprehensive strategy, integrating both national-level policy and individual action, positions Finland to effectively navigate the challenges of an increasingly complex security environment. The shared commitment to national defense, evident in both government initiatives and individual actions, underscores the strength and resilience of Finnish society in the face of evolving geopolitical realities.