Jean-Marie Le Pen: A Life of Controversy and Influence (Part 1 of 2)
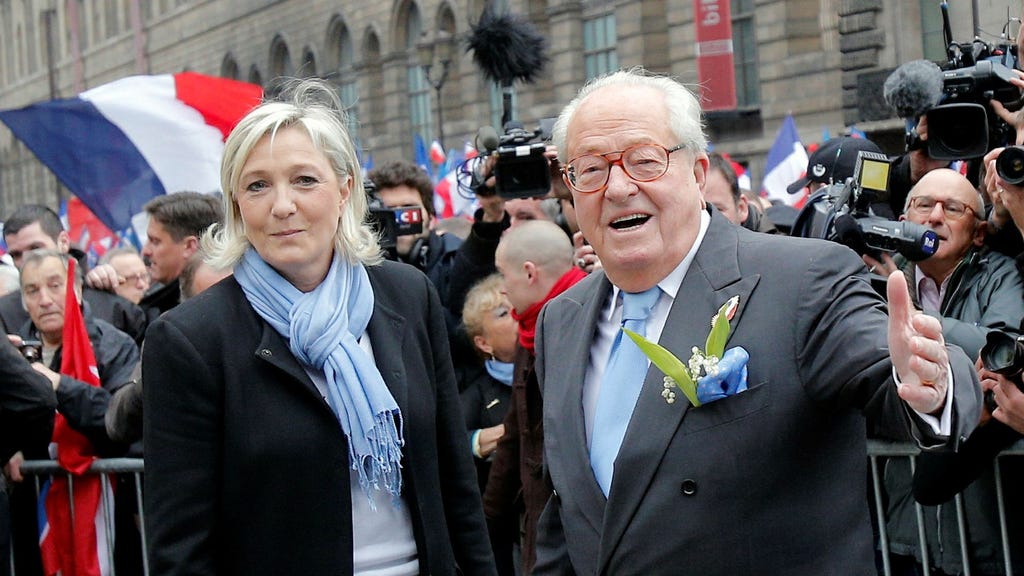
Jean-Marie Le Pen, nicknamed "Menhir" (standing stone), a moniker reflecting his steadfast and often unyielding nature, left an undeniable mark on French politics. From his initial foray into the political arena in 1956 until his passing in 2023, his career was a whirlwind of controversy, provocation, and outspoken pronouncements. Born in the summer of 1928 in the fishing village of La-Trinité-sur-Mer, Brittany, Le Pen’s early life was marked by both academic promise and disciplinary challenges. His intelligence was undeniable, but his rebellious spirit led to expulsions from several schools. Following his legal studies in Paris, he became the president of a student association, foreshadowing his future leadership roles.
Le Pen’s political trajectory took a decisive turn in 1972 with the formation of the National Front (Front National). This right-wing populist party, often categorized as far-right by scholars, served as his platform for five presidential bids. His greatest electoral success came in 2002, when he reached the second round of voting, garnering 17.8% of the vote. This unprecedented result shocked the French establishment and signaled a significant shift in the political landscape. Although he achieved a respectable 10.8% in the first round of the 2007 presidential election, his political influence gradually waned thereafter. In 2011, his daughter, Marine Le Pen, assumed leadership of the party, marking a generational shift and a potential softening of the party’s image.
Le Pen’s later years were punctuated by health concerns, particularly related to his heart, often keeping his name in the public eye. While largely withdrawing from active political commentary, he nevertheless acknowledged and congratulated the electoral successes of Rassemblement National (National Rally), the rebranded name of his party adopted in 2018. This rebranding, spearheaded by his daughter, represented an attempt to distance the party from its more controversial past and broaden its appeal. Despite his declining health, Le Pen remained a symbolic figure for a segment of the French population.
Jean-Marie Le Pen: A Life of Controversy and Influence (Part 2 of 2)
Le Pen’s death in a hospital in Garches, Hauts-de-Seine, after weeks of medical care marked the end of a tumultuous era in French politics. His daughter, Marine, learned of his passing during a layover while returning from Mayotte, a French overseas department north of Madagascar recently devastated by a cyclone. This unfortunate timing underscored the complex and often strained relationship between father and daughter, both bound by familial ties and separated by diverging political strategies.
Le Pen’s final resting place is planned to be the family plot in the cemetery of Trinité-sur-Mer, alongside his father. His desire for a simple gravestone bearing only his first name, as revealed in a 2018 interview with L’Express, suggests a desire for a less complex legacy. This contrasts with the multifaceted and often controversial nature of his public persona. His autobiography, also published in 2018, offers a glimpse into his personal sentiments, portraying himself as a saddened man witnessing the "shrinking" and "complete transformation" of his country.
Le Pen’s political philosophy was anchored in nationalist and often anti-immigration sentiments. He frequently clashed with established political norms and sparked numerous controversies throughout his career. His rhetoric often targeted immigration, globalization, and what he perceived as the decline of traditional French values. While his critics condemned his views as divisive and xenophobic, his supporters saw him as a defender of French identity and a bulwark against societal changes they viewed as detrimental.
Le Pen’s legacy remains a complex and contested one. He undeniably shaped the discourse on immigration and national identity in France, pushing these issues to the forefront of political debate. His impact extends beyond his own party, influencing the platforms of other right-wing movements across Europe. While his methods and pronouncements were often met with condemnation, he undoubtedly resonated with a segment of the French population who felt unheard and marginalized by mainstream politics. His influence, though waning in his later years, continues to reverberate through the political landscape of France and beyond. His life and career serve as a case study in the rise of populism, the power of provocative rhetoric, and the enduring tensions surrounding national identity in a globalized world. Understanding his impact requires not only an examination of his actions but also an acknowledgement of the societal anxieties that fueled his rise to prominence.