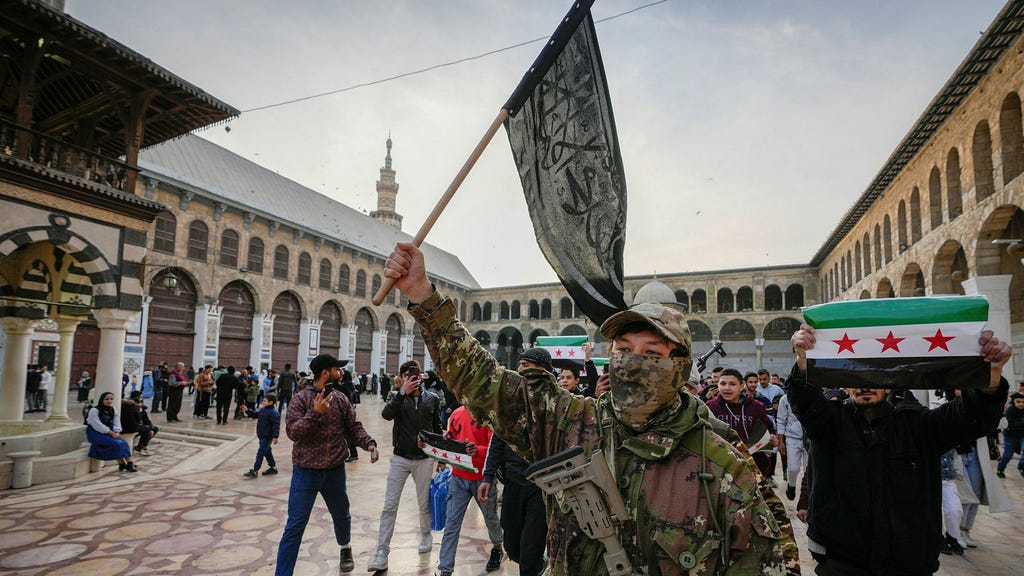
The Washington Post has reported that Ukraine supplied 150 drones and deployed 20 drone operators to Idlib, Syria, about a month ago, to support the Islamist HTS militia. This group is designated as a terrorist organization by the United States, the United Nations, and other countries. The Kyiv Post, another Ukrainian media outlet, also cited sources confirming Ukrainian intelligence support for the rebels over the past year. While Ukraine has not officially confirmed these reports, they have denied Russian claims of Ukrainian personnel being present in Idlib. This alleged support raises complex questions about Ukraine’s alliances and strategic objectives in the context of the ongoing conflict with Russia. The involvement of Ukrainian resources and personnel in a region riddled with complex geopolitical dynamics, including the presence of terrorist organizations, adds another layer to the already intricate Syrian conflict and the broader global fight against terrorism.
A rebel fighter, Suheil Hammoud, who previously fought with the Free Syrian Army until the overthrow of Bashar al-Assad, corroborated the reports of Ukrainian support in an interview with Ekot, a Swedish radio program. He confirmed the collaboration with Ukrainian special forces, citing a shared enemy in Russia as the basis for their cooperation. According to Hammoud, Ukrainian specialists provided digital training, facilitated by interpreters, to the rebels on operating military drones. He highlighted the effectiveness of drones for both Ukraine and the Syrian rebels, implying their crucial role in the ongoing conflicts in both regions. This direct testimony adds weight to the reports of Ukrainian involvement and sheds light on the specific nature of the support provided, focusing on the tactical advantage offered by drone technology.
Hammoud’s statement emphasizes the strategic rationale behind the alleged Ukrainian assistance, framing it within the larger context of resisting Russian influence. It underscores a potential pattern of Ukrainian engagement against Russian interests beyond its borders, mirroring similar reported actions in other parts of the world. This alignment of interests between Ukraine and certain Syrian rebel groups highlights the complex interplay of regional and international actors in the Syrian conflict, and further complicates the already challenging task of finding a peaceful resolution. The utilization of drone technology, as highlighted by Hammoud, indicates a shift towards asymmetric warfare tactics, where smaller forces can leverage technology to challenge larger, conventionally stronger adversaries.
While the Ukrainian support, primarily in the form of drone technology and training, has been acknowledged by some on the ground, its impact on the recent rebel offensive, spearheaded by HTS, remains debated. Most analysts believe that the Ukrainian contribution did not play a decisive role in the offensive’s outcome. However, this support can be interpreted as part of a broader Ukrainian strategy to challenge Russian interests and influence across the globe, beyond the immediate conflict within Ukraine’s borders. This strategic approach suggests a proactive stance by Ukraine, utilizing its resources and expertise to counter Russian activities in various theaters, potentially creating pressure points and diverting Russian resources.
The alleged Ukrainian involvement in Syria connects to broader patterns of Ukrainian activity against Russian interests in other regions. Reports indicate that Ukraine played a role in an incident in Mali last summer, where approximately 80 Russian Wagner mercenaries were killed. The Ukrainian intelligence service later claimed to have provided intelligence support that facilitated the attack. This pattern of activity suggests a broader, more proactive Ukrainian strategy aimed at disrupting Russian operations and influence, particularly those involving the Wagner Group, a private military company often linked to Russian interests.
The confluence of these reports paints a picture of Ukraine’s increasingly assertive foreign policy, extending its efforts to counter Russian influence beyond its own borders. While the efficacy of these actions remains subject to debate, they represent a significant shift in Ukraine’s strategic posture. By providing support to groups opposing Russian interests in various regions, Ukraine is actively seeking to weaken Russia’s global standing and disrupt its operations. This proactive approach represents a calculated risk, with potential implications for international relations and the ongoing conflicts in affected regions, demanding careful consideration and further analysis. This evolving dynamic adds another layer of complexity to the global geopolitical landscape, demanding continued monitoring and analysis to understand its long-term implications. The use of proxies and the provision of military support, even to controversial groups, raises ethical and strategic questions that warrant further scrutiny. The implications of these actions extend beyond the immediate conflicts, potentially impacting regional stability and the wider international order.